Workforce housing is a critical issue that intersects with urban planning in significant ways. As cities continue to grow and evolve, the need for affordable housing options for middle-income workers—such as teachers, healthcare workers, and first responders—becomes increasingly urgent. Urban planning plays a pivotal role in addressing these needs, ensuring that cities can accommodate their workforce while fostering sustainable and inclusive communities. This article explores the future of workforce housing through the lens of urban planning, highlighting key trends, challenges, and strategies.
The Growing Demand for Workforce Housing
The demand for workforce housing has been on the rise, driven by the increasing cost of living in urban areas. As property values and rents soar, middle-income workers often find themselves priced out of the housing market, forced to live further from their workplaces, which can lead to longer commutes and reduced quality of life. This disconnect between housing affordability and proximity to work is a significant issue that urban planners must address.
Urban planners are increasingly focused on creating mixed-use developments that include affordable housing options within city centers. These developments aim to provide housing for workers close to employment hubs, reducing commute times and fostering a better work-life balance. By integrating workforce housing into the fabric of urban development, cities can become more inclusive and resilient.
Incorporating Workforce Housing into Urban Planning
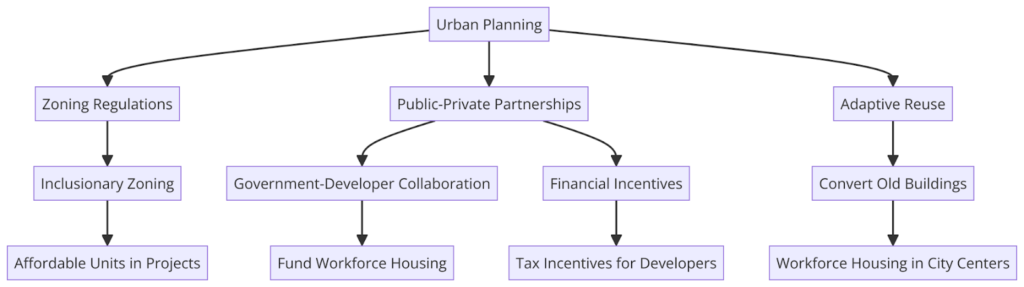
Urban planning strategies must be proactive in incorporating workforce housing into city development plans. This involves zoning regulations that incentivize the construction of affordable housing units, as well as public-private partnerships that bring together city governments, developers, and community organizations.
In many cities, inclusionary zoning laws require developers to include a percentage of affordable units in new residential projects. These regulations are designed to ensure that as cities grow, they do so in a way that is accessible to workers across various income levels. Additionally, urban planners are exploring the potential of adaptive reuse—converting underutilized buildings, such as old office spaces or warehouses, into workforce housing.
Challenges in Providing Workforce Housing
Despite the clear need for workforce housing, several challenges hinder its development. One of the most significant barriers is the high cost of land in urban areas, which can make affordable housing projects financially unfeasible. Developers often face difficulties in securing funding for such projects, especially in competitive real estate markets.
Another challenge is community opposition, sometimes referred to as NIMBYism (Not In My Backyard). Residents in certain neighborhoods may resist the development of affordable housing, fearing it could lower property values or change the character of their community. Overcoming these challenges requires effective communication and engagement with the community to demonstrate the benefits of workforce housing for the entire city.
Innovative Solutions in Workforce Housing
To address the challenges associated with workforce housing, urban planners and developers are exploring innovative solutions. One such approach is the use of modular construction, which allows for faster and more cost-effective building processes. Modular housing units are prefabricated in a factory and then assembled on-site, reducing construction time and costs.
Another innovative solution is the development of transit-oriented housing. By building affordable housing near public transit hubs, cities can provide workers with easy access to transportation, reducing the need for car ownership and making commuting more efficient. This approach supports workforce housing and promotes sustainable urban development by reducing traffic congestion and lowering carbon emissions.
The Role of Public-Private Partnerships
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) are crucial in the development of workforce housing. These collaborations bring together the resources and expertise of both the public and private sectors to create affordable housing solutions that might not be possible through traditional funding methods alone. PPPs can leverage public land or provide tax incentives to developers in exchange for the construction of affordable housing units.
For example, some cities offer density bonuses, allowing developers to build more units than typically permitted in exchange for including a certain percentage of affordable housing. These incentives can make workforce housing projects more financially viable for developers while helping cities meet their housing needs.
The Impact of Technology on Workforce Housing
Technology is playing an increasingly important role in the planning and development of workforce housing. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and data analytics are being used to identify areas with the greatest need for affordable housing and to plan developments that maximize access to essential services, such as schools, healthcare, and public transit.
In addition to planning, technology is also impacting the construction process. Advanced building materials, energy-efficient designs, and smart home technologies are being integrated into workforce housing developments to create more sustainable and cost-effective living spaces. These innovations reduce the environmental impact of housing and lower utility costs for residents, making housing more affordable in the long term.
The Future of Workforce Housing in Urban Planning
The future of workforce housing will depend on the ability of urban planners, developers, and policymakers to collaborate and innovate. As cities continue to grow, the need for affordable housing solutions that cater to middle-income workers will become even more pressing. Urban planning will need to be flexible and forward-thinking, incorporating new technologies, innovative construction methods, and inclusive policies to meet this demand.
Moreover, workforce housing should not be seen as a separate or secondary aspect of urban development but rather as an integral component of creating vibrant, diverse, and sustainable communities. By prioritizing workforce housing in urban planning, cities can ensure that all residents have access to safe, affordable, and convenient housing options.
In Conclusion
Workforce housing is a critical issue that intersects with many aspects of urban planning. As cities face increasing pressure to accommodate growing populations, the need for affordable housing for middle-income workers becomes ever more urgent. Through innovative solutions, public-private partnerships, and the thoughtful integration of workforce housing into urban development plans, cities can create more inclusive and sustainable communities. The future of workforce housing will require ongoing collaboration, creativity, and commitment from all stakeholders involved in urban planning and development.

Thomas J. Powell is a distinguished Senior Advisor at Brehon Strategies and a recognized figure in the realm of entrepreneurship and private equity. His journey in the financial services and banking sector, starting in 1988 in Silicon Valley, spans more than 35 years and is marked by profound industry expertise. Powell’s dual citizenship in the European Union and the United States empowers him to adeptly steer through international business landscapes. Currently studying for his Doctor of Law and Policy at Northeastern University, his research is centered on addressing the shortage of middle-income workforce housing in rural resort areas. Alongside his professional pursuits, he remains committed to community enrichment, illustrated by his 45-year association with the Boys and Girls Clubs of America. Follow Thomas J Powell on Twitter, Linkedin etc.

