Green urbanism represents a visionary approach to city planning and development, one that harmonizes human activities with the natural environment. It’s an ethos that prioritizes sustainability, ensuring urban growth contributes positively to the health of our planet. This concept is increasingly crucial as we face global environmental challenges that threaten our way of life. Climate change, urban sprawl, and the loss of biodiversity are just a few issues that green urbanism seeks to address. By fostering communities that are both beneficial to humans and the environment, we can create resilient, vibrant cities that thrive in harmony with nature.
The urgency for adopting green urbanism cannot be overstated. As urban populations grow, the strain on resources and ecosystems intensifies, making sustainable urban development not just desirable but essential. This article aims to delve into the principles of green urbanism, offering insights into its implementation and the myriad benefits it brings. From reducing our carbon footprint to promoting biodiversity and enhancing residents’ quality of life, green urbanism presents a path forward that aligns with both our developmental aspirations and environmental responsibilities.
Fundamentals of Green Urbanism
Core Principles of Green Urbanism
Green urbanism is built on several foundational principles that guide sustainable urban development. Energy efficiency stands at the forefront of this movement. By designing buildings and infrastructures that minimize energy consumption, cities can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and mitigate their impact on climate change. This principle extends beyond mere energy conservation to encompass the generation of renewable energy, supporting a transition towards a more sustainable energy future.
Reducing the carbon footprint of urban areas is another critical aspect of green urbanism. This involves not only energy-efficient buildings but also comprehensive urban planning that minimizes waste, promotes recycling, and encourages the use of sustainable materials. Enhancing green spaces within urban areas, such as parks, green roofs, and community gardens, is vital for preserving biodiversity, improving air quality, and providing residents with valuable recreational spaces.
Promoting sustainable transportation is also a key element of green urbanism. Encouraging the use of public transportation, cycling, and walking over personal vehicles helps reduce traffic congestion, lower emissions, and improve the overall health and well-being of urban residents. By integrating these principles, cities can forge a sustainable path forward, balancing development with environmental preservation.
The Role of Technology in Green Urbanism
Modern technologies play a pivotal role in enabling and advancing the goals of green urbanism. Smart grids, for example, revolutionize how cities manage energy distribution, allowing for more efficient use of renewable energy sources and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Green building materials, such as recycled steel, bamboo, and low-emission glass, offer sustainable alternatives that reduce the environmental impact of construction projects.
In addition to these, advancements in information and communication technologies (ICT) facilitate smarter urban planning and management. IoT (Internet of Things) sensors can monitor air quality, water usage, and energy consumption in real-time, providing data that can inform more sustainable urban practices. Moreover, technology-driven solutions such as green infrastructure and water-sensitive urban design play a crucial role in managing stormwater, reducing urban heat islands, and enhancing urban biodiversity.
The integration of technology in urban planning and development is not just about environmental sustainability; it also opens up new avenues for economic growth and social inclusion, making cities more livable, resilient, and adaptable to the challenges of the 21st century. As we delve deeper into the principles and practices of green urbanism, it becomes clear that the thoughtful application of technology is key to achieving a sustainable urban future.
Strategies for Sustainable Urban Development
Energy-Efficient Urban Planning
Energy efficiency is a cornerstone of sustainable urban development, emphasizing the need for buildings and communities to minimize their environmental footprint through intelligent design and construction practices. Techniques for achieving energy efficiency include the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, into building designs. This not only reduces reliance on fossil fuels but also decreases energy costs in the long term. Additionally, the implementation of green building standards, like LEED or BREEAM, ensures that new constructions adhere to high energy efficiency and environmental sustainability criteria. Insulation, energy-efficient lighting, and HVAC systems further contribute to reducing energy consumption, while smart city technologies allow for the monitoring and management of energy use in real-time, ensuring optimal performance across urban landscapes.
Promoting Green Spaces
Green spaces play a vital role in enhancing urban livability and biodiversity. They offer a myriad of benefits, including air purification, temperature regulation, and providing habitats for urban wildlife. The development of parks, green roofs, and vertical gardens not only contributes to the aesthetic appeal of urban areas but also supports residents’ mental and physical well-being by offering spaces for recreation and relaxation. Urban planners and developers can incorporate green spaces into city landscapes by prioritizing the preservation of natural areas and integrating plant life into building designs. Community gardens and urban farms also promote local food production, reducing the carbon footprint associated with food transportation and providing residents with fresh produce.
Sustainable Transportation Solutions
Transitioning to sustainable transportation systems is essential for reducing urban congestion and pollution. Encouraging the use of public transport, cycling, and walking over personal vehicles can significantly lower carbon emissions and improve air quality. Urban planning strategies that support this shift include the development of extensive and efficient public transportation networks, the creation of bike lanes and pedestrian paths, and the implementation of bike-sharing and car-sharing programs. Additionally, policies such as congestion pricing and limited parking in city centers can incentivize the use of greener transportation options. Integrating transportation planning with land use decisions ensures that communities are designed to be walkable and transit-oriented, making sustainable transportation choices more accessible and convenient for residents.
Balancing Development and Environmental Sustainability through Green Urbanism
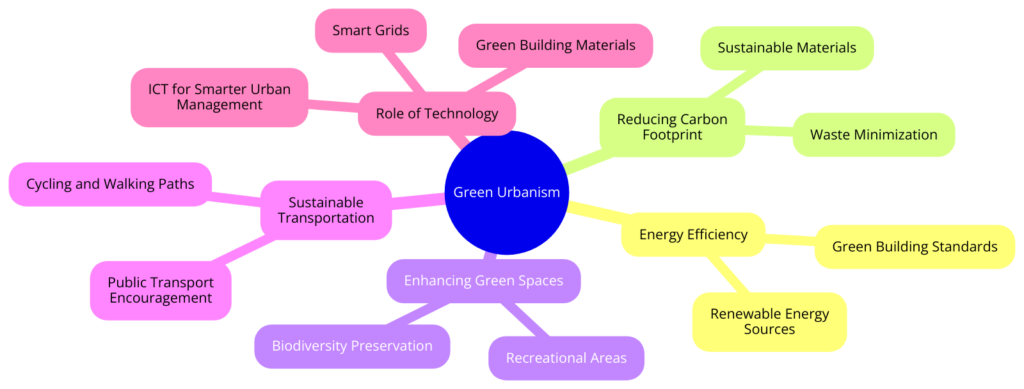
Green Urbanism represents a transformative approach to urban planning, where the focus is on creating spaces that are in harmony with the natural environment. It emphasizes sustainable growth, aiming to reduce the ecological footprint of cities while enhancing the quality of life for their residents.
Core Principles of Green Urbanism
The principles of Green Urbanism, as depicted in the mindmap, are foundational to achieving a sustainable urban future. These include:
- Energy Efficiency: Incorporating renewable energy sources and green building standards to minimize energy consumption.
- Reducing Carbon Footprint: Implementing waste minimization strategies, promoting recycling, and using sustainable materials in construction to lower urban areas’ carbon emissions.
- Enhancing Green Spaces: Creating parks, green roofs, and community gardens to preserve biodiversity, improve air quality, and provide recreational areas for residents.
- Promoting Sustainable Transportation: Encouraging the use of public transport, biking, and walking to reduce traffic congestion and emissions.
- The Role of Technology: Utilizing smart grids, green building materials, and ICT to enhance urban management and support sustainable practices.
The Impact of Green Urbanism
Green Urbanism not only addresses environmental challenges but also offers numerous benefits for urban dwellers. By integrating green spaces into city landscapes, promoting energy-efficient infrastructure, and encouraging sustainable modes of transportation, cities can improve air and water quality, enhance residents’ health and well-being, and create more resilient and vibrant communities.
Implementing Green Urbanism
Adopting Green Urbanism requires a holistic approach that involves policymakers, urban planners, businesses, and the community. Strategies for implementation include:
- Policy and Planning: Developing policies and guidelines that support sustainable urban development.
- Community Engagement: Involving citizens in the planning process to ensure projects meet the community’s needs and preferences.
- Innovation and Technology: Leveraging technology and innovation to optimize resource use and enhance urban sustainability.
The Future of Urban Planning
The future of urban planning under the principles of Green Urbanism is promising. As cities continue to grow, integrating sustainable practices into urban development will be crucial for ensuring that cities are livable, environmentally friendly, and economically vibrant. The adoption of Green Urbanism practices worldwide signifies a commitment to building a sustainable future for generations to come.
Green Urbanism presents a pathway towards sustainable urban development, balancing the needs of the environment with those of a growing urban population. By embracing the principles outlined in the mindmap, cities can navigate towards sustainability, ensuring a greener, more prosperous future for urban environments.
5 Innovative Green Urbanism Projects Around the World
1. Copenhagen, Denmark
Copenhagen is at the forefront of green urbanism, with a commitment to becoming carbon-neutral by 2025. The city’s approach includes extensive bike lanes, green roofs, and renewable energy initiatives. Copenhagen’s bicycle infrastructure is world-renowned, with over 390 kilometers of bike lanes, encouraging a culture where more than half of the city’s residents commute by bike.
2. Singapore
Known as the “Garden City,” Singapore has integrated green spaces into its urban fabric, with projects like the Gardens by the Bay and the incorporation of vertical gardens in residential and commercial buildings. The city-state’s emphasis on green building certifications and its investment in public transport further underscore its commitment to sustainable urban development.
3. Freiburg, Germany
Freiburg is celebrated for its sustainable urban planning and energy-efficient housing. The Vauban district, in particular, is a model of green urbanism, featuring car-free zones, solar-powered homes, and a strong community focus on sustainability. Freiburg’s comprehensive tram system and green spaces encourage active, eco-friendly lifestyles among its residents.
4. Curitiba, Brazil
Curitiba’s innovative urban planning includes a renowned bus rapid transit system, extensive parks, and green belts that double as flood prevention. The city has implemented recycling programs and pedestrian-only zones, making it a model for sustainable urban development in Latin America.
5. Vancouver, Canada
Vancouver aims to be the greenest city in the world by 2020. Initiatives include green building requirements, the expansion of cycling and pedestrian infrastructure, and the development of green jobs. The city’s focus on renewable energy and urban greenery exemplifies its commitment to combining urban growth with environmental stewardship.
These examples of green urbanism projects around the world demonstrate the varied and innovative approaches cities are taking to balance development with environmental sustainability. By learning from these models, other cities can implement similar strategies to enhance the livability, sustainability, and resilience of their urban environments.
The Future of Urban Development
Evolving Trends in Green Urbanism
The landscape of urban development is rapidly evolving, with green urbanism at the forefront of shaping sustainable cities of the future. Emerging trends such as biophilic design, which integrates natural elements into urban settings, are gaining traction. This approach not only enhances aesthetic appeal but also promotes health and well-being among urban dwellers. Another significant trend is the rise of smart cities that leverage IoT (Internet of Things) technologies to optimize resource use and reduce waste. These technologies enable cities to monitor air quality, energy consumption, and traffic flow in real-time, making urban living more sustainable.
The push towards zero-carbon cities is another trend shaping the future of urban development. This involves transitioning to renewable energy sources, enhancing energy efficiency, and adopting green transportation options. Urban agriculture is also emerging as a key component of green urbanism, with rooftop gardens and vertical farms reducing the carbon footprint associated with food production and transportation.
Overcoming Challenges in Sustainable Urban Planning
Despite the promising outlook, sustainable urban planning faces several challenges. Funding remains a significant barrier, with many green initiatives requiring substantial upfront investment. However, innovative financing models such as green bonds and public-private partnerships are emerging to address this issue. Policy constraints and bureaucratic hurdles can also impede the implementation of sustainable projects. Streamlining regulatory processes and fostering collaboration between government entities, developers, and the community is essential for overcoming these obstacles.
Community involvement is crucial in the successful implementation of green urbanism projects. Engaging citizens in the planning process ensures that projects meet the community’s needs and garner public support. Education and awareness campaigns can also play a pivotal role in promoting sustainable practices among residents.
The Economic Case for Green Urbanism
The economic benefits of investing in sustainable urban development are increasingly recognized. Contrary to the myth that green initiatives are prohibitively expensive, evidence suggests that sustainable urbanism can lead to significant long-term savings. Energy-efficient buildings, for example, result in lower utility costs, while green infrastructure can reduce expenses related to stormwater management. Moreover, sustainable urban development can enhance property values, attract investment, and create green jobs, contributing to economic growth. By analyzing the long-term economic advantages, it’s clear that the investment in green urbanism not only pays off but is also essential for the financial sustainability of urban areas.
Some FAQs Answered on The Relevant Topic
How can cities balance economic growth with environmental sustainability?
Cities can achieve this balance by integrating sustainable practices into economic development strategies. Investing in green infrastructure, promoting clean energy, and encouraging sustainable industries can drive economic growth while preserving the environment.
What are the first steps a city should take towards becoming more ‘green’?
Initial steps include conducting an environmental audit to identify areas for improvement, setting clear sustainability goals, and developing a comprehensive green urbanism plan. Engaging the community and stakeholders in this process is also crucial.
How can individuals contribute to the goal of green urbanism?
Individuals can contribute by adopting sustainable practices, such as using public transportation, reducing waste, supporting local green businesses, and participating in community sustainability initiatives.
What are the main barriers to implementing green urbanism practices?
Barriers include limited funding, regulatory hurdles, lack of public awareness, and resistance to change. Overcoming these requires innovative financing, policy reform, community engagement, and education.
Conclusion: A Greener Future for Urban Development
The journey towards green urbanism is both a challenge and an opportunity to reimagine our cities as sustainable, resilient, and vibrant communities. This article has explored key strategies, innovative projects, and the economic rationale behind sustainable urban development, emphasizing the importance of a holistic approach that encompasses energy efficiency, green spaces, sustainable transportation, and smart technologies. As we look to the future, it’s clear that a collective effort from policymakers, developers, and citizens is crucial for realizing the vision of green urbanism. By embracing the principles outlined, cities can navigate the path towards sustainability, ensuring a greener, more prosperous future for urban development.

Thomas J. Powell is a distinguished Senior Advisor at Brehon Strategies and a recognized figure in the realm of entrepreneurship and private equity. His journey in the financial services and banking sector, starting in 1988 in Silicon Valley, spans more than 35 years and is marked by profound industry expertise. Powell’s dual citizenship in the European Union and the United States empowers him to adeptly steer through international business landscapes. Currently studying for his Doctor of Law and Policy at Northeastern University, his research is centered on addressing the shortage of middle-income workforce housing in rural resort areas. Alongside his professional pursuits, he remains committed to community enrichment, illustrated by his 45-year association with the Boys and Girls Clubs of America. Follow Thomas J Powell on Twitter, Linkedin etc.

