In recent years, the escalating issue of housing affordability has emerged as a critical challenge, particularly impacting the workforce in urban areas. As cities grow and evolve, the gap between the availability of affordable housing and the needs of the working population has widened significantly. This disparity not only affects the economic fabric of urban centers but also has profound implications on the lives and well-being of countless individuals who power these metropolitan engines.
The challenges of securing affordable housing extend beyond the realm of personal inconvenience; they strike at the heart of workforce productivity and overall quality of life. Employees grappling with long commutes or unstable living situations often face increased stress, reduced job satisfaction, and diminished health, all of which can impact workplace performance. The need for affordable housing solutions is not just a social concern but a critical economic issue.
This article seeks to delve into the innovative solutions and strategies currently being implemented to bridge the housing gap for the workforce. Our exploration will encompass a range of initiatives from both the public and private sectors, highlighting how collaboration, creativity, and commitment are being leveraged to tackle this pressing issue. From reimagining urban living spaces to leveraging technology in construction, the focus will be on pragmatic, forward-thinking solutions making a real difference in communities across the globe.
Understanding the Housing Challenge
The issue of housing affordability is a complex puzzle, with numerous pieces contributing to the current state of crisis, particularly in urban environments.
The Current State of Housing Affordability
In many cities around the world, the cost of housing has skyrocketed, outpacing the growth in wages and making it increasingly difficult for the workforce to find affordable living spaces. This situation is compounded by the trend of urbanization, with more people flocking to cities in search of employment, thereby intensifying the demand for housing. The result is a market where the supply of reasonably priced homes falls dramatically short of demand, forcing many into long commutes or inadequate living conditions.
Factors Contributing to the Housing Gap
Several key factors contribute to this growing divide. First, urbanization has led to increased demand for housing in cities, often outstripping supply and driving up prices. Secondly, the rising costs of land and construction materials make it challenging to develop affordable housing options. Income disparity also plays a significant role; as wages in many sectors have not kept pace with the rising cost of living, a significant portion of the urban workforce finds itself priced out of the housing market.
These factors combine to create a scenario where affordable housing is not just a commodity but a vital necessity for the stability and growth of urban centers and their inhabitants. Addressing this challenge requires a multi-faceted approach, considering economic, social, and developmental perspectives to devise solutions that are sustainable, equitable, and effective.
Innovative Solutions in Housing
Implementing Innovative Housing Solutions
Communities and businesses face the challenge of providing affordable housing while balancing economic viability and sustainability. Implementing innovative housing solutions requires strategic planning, community engagement, and embracing new technologies.
- Assessing Community Needs: Start by understanding the specific housing needs of your community. Engage with residents, conduct surveys, and analyze demographic data to identify the types of housing most in demand.
- Collaborating with Local Governments: Partner with local government bodies to gain support for housing projects. This can include securing land, obtaining necessary permits, and discussing potential tax incentives or subsidies.
- Utilizing New Building Technologies: Embrace innovative construction technologies like modular building and 3D printing to reduce construction time and costs. These methods can provide quality housing at a fraction of the cost and time of traditional construction.
- Funding and Investment: Explore various funding options, including private investments, public grants, and crowdfunding. Financial viability is key to the success of affordable housing projects.
- Community Involvement: Involve the community in the planning and development process. This ensures the housing solutions meet the actual needs and fosters a sense of ownership among residents.
- Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Practices: Incorporate sustainable building practices and materials. Energy-efficient designs and green spaces can make housing more affordable in the long run and reduce environmental impact.
The Widening Gap: Housing Affordability Crisis in Urban Centers
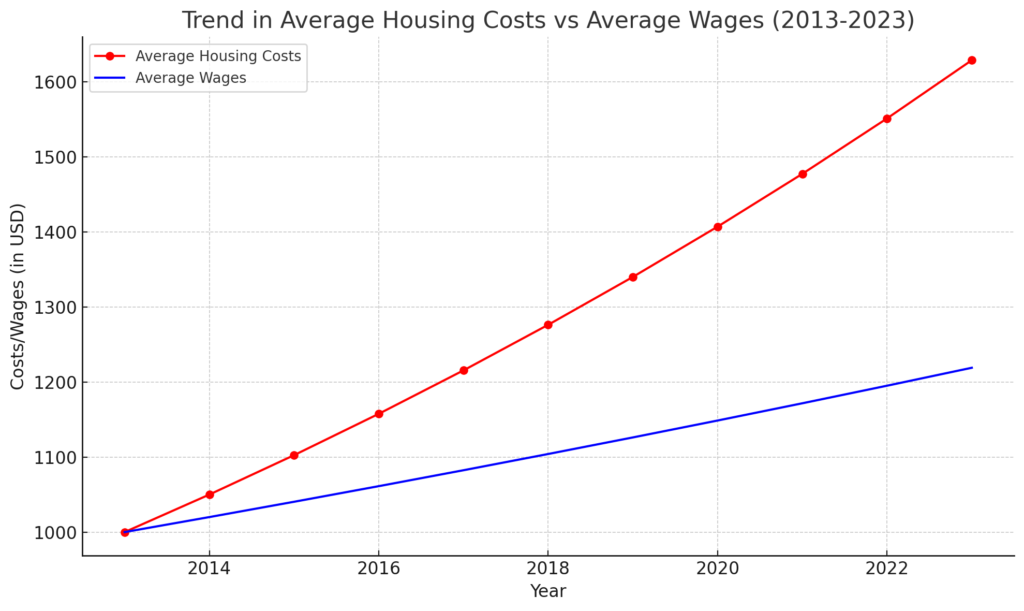
The graph above strikingly illustrates the escalating crisis in housing affordability in urban areas from 2013 to 2023. It shows a consistent and worrying trend: while average housing costs have seen a significant upward trajectory, the growth in average wages has been far more modest. This divergence has resulted in a widening gap that underpins the affordability crisis faced by many urban dwellers.
Over the last decade, the average housing costs have surged at a rate that far outpaces wage increases. This disparity is not just a matter of economic statistics; it reflects a reality where increasing numbers of individuals and families find it challenging to secure affordable housing in urban centers. The implications of this trend are profound, affecting not only the quality of life for residents but also the social and economic fabric of cities.
The issue is multifaceted, driven by factors such as rapid urbanization, rising land and construction costs, and the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, which altered work and living patterns. The shift towards remote work has also influenced housing demand, particularly in suburban areas, exacerbating the affordability issue in urban centers.
The growing housing affordability crisis calls for urgent and innovative solutions. It highlights the need for policy interventions that focus on increasing the supply of affordable housing, revising zoning laws, and ensuring that wage growth keeps pace with the cost of living. Private and public sector collaboration is crucial to address these challenges effectively.
As urban centers continue to grow, ensuring that housing remains accessible and affordable for all segments of the workforce is not just a social imperative but a critical component in maintaining the vitality and sustainability of our cities. The graph not only presents a stark reality but also serves as a call to action for policymakers, developers, and community leaders to bridge the growing gap between housing costs and wages.
Top 5 Innovative Housing Models
1. Co-living Spaces for Urban Professionals
Co-living spaces are becoming increasingly popular in urban areas. These shared living arrangements offer affordable, flexible housing options, especially for young professionals and students. Co-living spaces often include shared amenities like kitchens and lounges, fostering a sense of community and networking opportunities.
2. Modular and Prefabricated Homes
Modular and prefabricated homes are revolutionizing the construction industry. These homes are built off-site and assembled on location, significantly reducing construction time and cost. They offer a viable solution for rapidly deploying affordable housing without compromising on quality.
3. Public-Private Partnerships for Mixed-Use Developments
Public-private partnerships are essential in developing mixed-use projects that combine residential, commercial, and sometimes industrial spaces. These developments can revitalize communities, provide affordable housing, and stimulate economic growth.
4. Rent-to-Own Schemes
Rent-to-own schemes offer a pathway to homeownership for individuals who cannot afford the upfront costs. These arrangements allow residents to rent a property with the option to buy it after a certain period, with a portion of their rent going towards the purchase price.
5. Green and Sustainable Housing Projects
Sustainable housing projects focus on environmental responsibility and energy efficiency. These projects utilize renewable energy sources, sustainable materials, and green technology, reducing the overall living costs for residents and minimizing the environmental footprint.
Incorporating these innovative housing models can significantly address the affordability crisis in urban areas. By embracing new ideas and technologies, communities and businesses can create sustainable, affordable housing solutions that cater to diverse needs.
The Future of Workforce Housing
The landscape of workforce housing is at a pivotal juncture, with evolving work patterns and economic shifts shaping future trends. Industry experts offer valuable insights into how these changes are influencing housing solutions and what we can expect in the years ahead.
Insights on Future Housing Trends
The consensus among experts is that workforce housing will need to become more adaptable and flexible to keep pace with changing job markets and work modalities. With the rise of remote work, there’s an increasing demand for housing that supports work-from-home environments. This shift might lead to a greater emphasis on larger living spaces with dedicated work areas, high-speed internet access, and community amenities like co-working spaces.
Another trend is the growing importance of sustainability in workforce housing. Eco-friendly designs, energy-efficient systems, and green living spaces are not just environmental choices but also practical ones, reducing long-term living costs for residents and attracting environmentally conscious tenants.
Impact of Remote Work on Housing Solutions
The remote work revolution has significant implications for workforce housing. It’s reducing the need for workers to live near urban business centers, thereby lessening the pressure on housing markets in these areas. This decentralization could lead to a more even distribution of housing demand, potentially revitalizing suburban and rural areas and leading to new housing development strategies that cater to remote workers.
Some FAQs Answered On The Relevant Topic
What are the biggest challenges in providing affordable workforce housing?
Key challenges include the rising cost of land and construction, regulatory hurdles, and funding limitations. Addressing these requires coordinated efforts between government, developers, and communities to find cost-effective, sustainable solutions.
How can we ensure that workforce housing remains affordable in the long term?
Long-term affordability can be achieved through a combination of rent control policies, public subsidies, and innovative financing models that reduce the cost burden on tenants. Additionally, incorporating energy-efficient designs can lower living costs.
Is there a role for technology in developing workforce housing solutions?
Absolutely. Technology plays a crucial role, from using data analytics for identifying housing needs to employing construction technologies like modular building for cost and time efficiency. Smart home technologies can also enhance the living experience and efficiency of workforce housing.
In Conclusion
The innovative solutions and strategies explored in this article highlight the multifaceted approach needed to bridge the housing gap for the workforce. From embracing new building technologies to rethinking design for remote work, the future of workforce housing requires creativity, collaboration, and a commitment to sustainability. The importance of collaborative efforts among various stakeholders is paramount in addressing the challenges of housing affordability and ensuring that the workforce has access to suitable living conditions. As society continues to evolve, so must our strategies for housing, adapting to meet the changing needs of the workforce. It is incumbent upon government entities, private developers, community organizations, and other stakeholders to actively participate in creating and sustaining housing solutions that are both affordable and conducive to the modern way of living and working.

Thomas J. Powell is a distinguished Senior Advisor at Brehon Strategies and a recognized figure in the realm of entrepreneurship and private equity. His journey in the financial services and banking sector, starting in 1988 in Silicon Valley, spans more than 35 years and is marked by profound industry expertise. Powell’s dual citizenship in the European Union and the United States empowers him to adeptly steer through international business landscapes. Currently studying for his Doctor of Law and Policy at Northeastern University, his research is centered on addressing the shortage of middle-income workforce housing in rural resort areas. Alongside his professional pursuits, he remains committed to community enrichment, illustrated by his 45-year association with the Boys and Girls Clubs of America. Follow Thomas J Powell on Twitter, Linkedin etc.

